Dr. Levander is very familiar with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) treatment for patients who have not responded to prior antidepressant medication treatment. TMS is the first and only non-systematic and non-invasive treatment method for major depression that has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. TMS uses a highly focused, pulsed magnetic field to stimulate new neural functioning in areas of the brain affected by depression. It is offered to patients by prescription only and delivered under the supervision of a psychiatrist.
NeuroStar TMS Therapy® is:
— Non-invasive and doesn’t involve any type of surgery, anesthesia, or sedation.
— Has been proven safe and effective for treating patients with depression.
— Performed while you remain awake and alert. Patients and are able to resume normal activities upon leaving the treatment session.
— Non-systematic, meaning that treatment is not taken by mouth and does not circulate in the blood stream throughout your body.
— Free of side effects typically experienced with antidepressant medications. The most common side effect associated with TMS Therapy is localized pain or discomfort at or near the treatment area – generally mild to moderate.
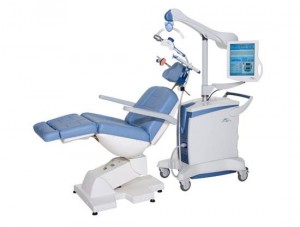 HOW IT WORKS
HOW IT WORKS
NeuroStar TMS Therapy® is a short outpatient procedure performed in a psychiatrist’s office or at a center established for the treatment of depression using the FDA approved Neurostar TMS machine. The treating clinician uses a treatment coil to send a pulsed magnetic field, similar in type and strength to magnetic fields produced by a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine, to the part of your brain thought to control mood.
TMS Therapy® is a highly targeted treatment reaching 2-3 centimeters into the brain, directly beneath the treatment coil. The nature of the magnetic field allows it to pass through a patient’s hair, skin and skull and into the mood-regulating area without being distorted in any way. This method allows for precise, targeted stimulation, minimizing the stimulation of brain tissue not involved in mood.
These magnetic pulses produce very small electrical currents. The amount of electricity created in the brain is very small and cannot be felt by a patient. These small electric currents can cause the neurons (brain cells) to fire or become active and lead to the release of neurotransmitters (the brain’s chemical messengers).